Do you have any idea what SAP Universal Journal is?
Home - SAP

SAP Universal Journal – One Single Source of Truth
Sonia Breton
Why did SAP introduce the Universal Journal?
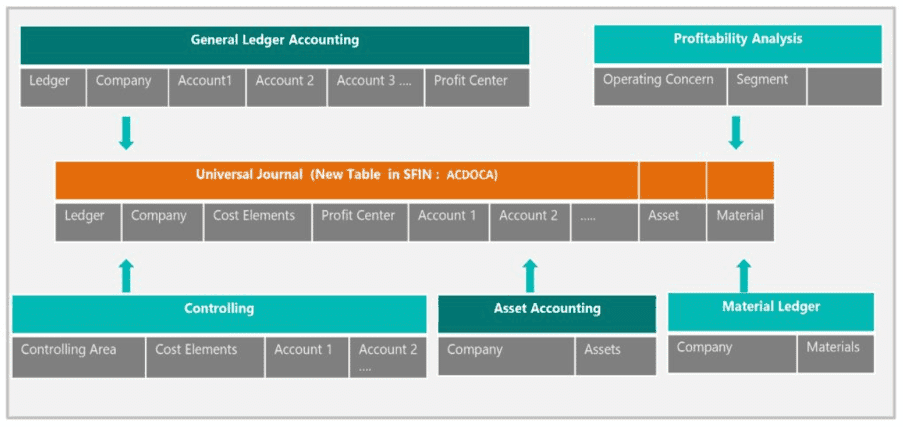
The Universal Journal was developed to combine into one source of data the once 2 separated Financial components:
- Financial Accounting (FI)
- Controlling (CO).
This single source of truth collects all accounting-relevant transactions into one table and makes them available to all relevant application components:
- Financial Accounting (General Ledger),
- Controlling,
- Asset Accounting,
- Material Ledger.
There is 1 combined FI / CO document linked with a logical document; all the information is recorded in 1 line item in table ACDOCA.
Wow! That’s a great deal of simplification! Thanks to SAP HANA database which is capable of compressing a lot of data and aggregating a huge number of line items in a spilt second, facilitating the process to dispense, with separate physical line item and totals tables in each application.
It also means that Financial Accounting and Managerial Accounting are reconciled constantly and the need for reconciliation between FI and the other Financials modules (CO or FI-AA) disappears along with the real-time integration of these components.
The reports in all components use data from the same journal, known as Universal Journal.
In the system
Master Data
Financials master data were fundamentally reorganized in order to have the Universal Journal up and running.
All cost elements (primary and secondary) are now merged in the G/L accounts. Therefore, we only need to maintain 1 master data that bears both the account and the cost element.
In the backend, transactions related Cost elements maintenance simply do not exist anymore.
Below screen-prints between ECC EHP6 for SAP ERP 6.0 and S/4HANA.
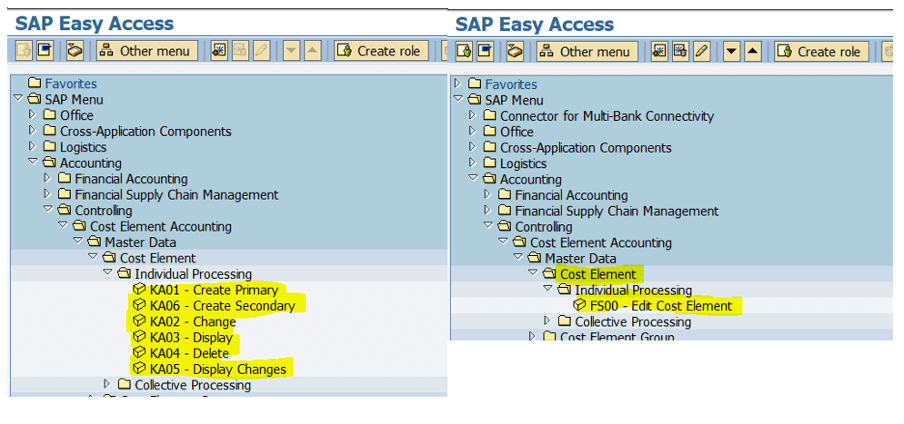
The old transactions are rerouted to transaction FS00 Edit Cost Element.
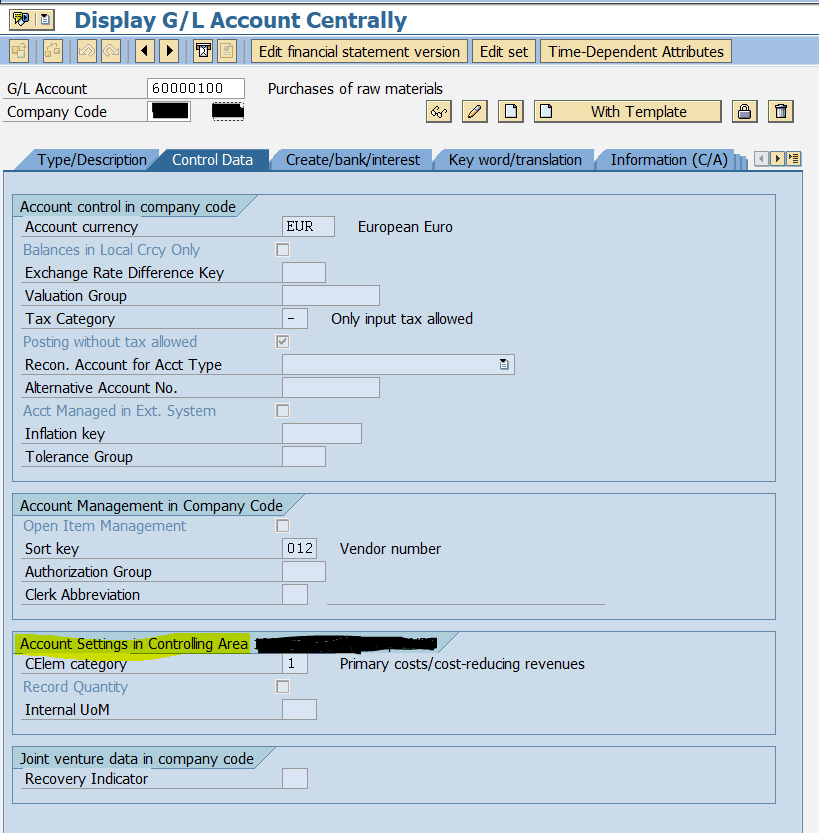
In Fiori, you only have to set up application to edit G/L account (FXXX). When editing a G/L account, the Control Data tab now includes the parameters for the Account settings in the Controlling area, revealing without any doubts that the cost element and the account are only one master data.
Posting of a document
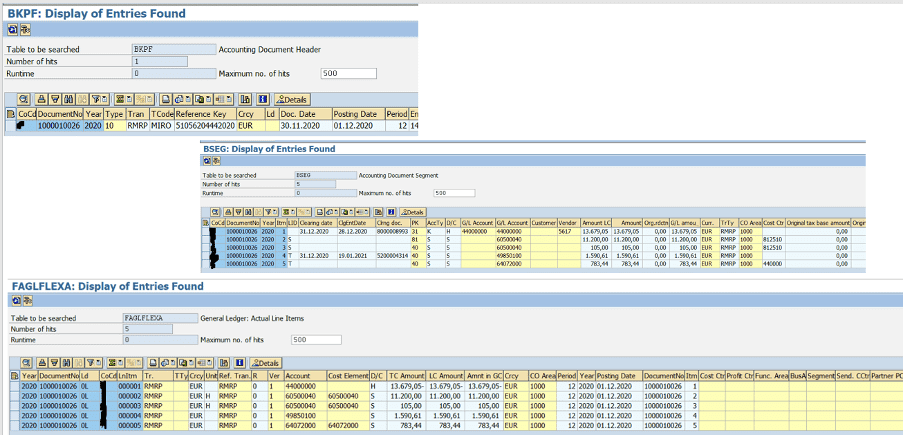
In ECC, when you post an FI document, entries in BSEG, FAGLFLEXA, FAGLFLEXT, COBK, COEJ and COEP tables (and some more BSIS, etc) are generated.
In S/4HANA, all the information are recorded in BKPF (header) and ACDOCA (line items), reducing significantly the number of tables impacted and thus, facilitating data reconciliation and reporting.
The old tables are no longer updated but, magically the old reports are still working (for example FAGLL03 or FBL*N) because compatibility views for a data request from one of these tables read the data from ACDOCA. But, if you are using Fiori, you mind as well use the new reports since those applications are way more faster and will deliver more details than the old reports.
What will happen to old tables?
Updates are no longer made to these old tables.
Nevertheless, you can continue to use reports that use data from these old tables. This is because compatibility views for a data request from one of these tables read the data from ACDOCA. Nevertheless, it is best to use the new Fiori application to display the data since it is faster than the old reports.
Let’s have a look at the views in these ECC tables with ACDOCA.
FI tables
CO tables
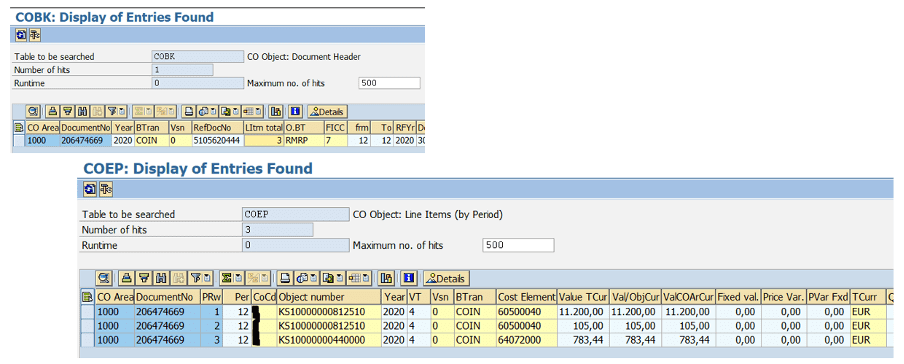
S/4HANA
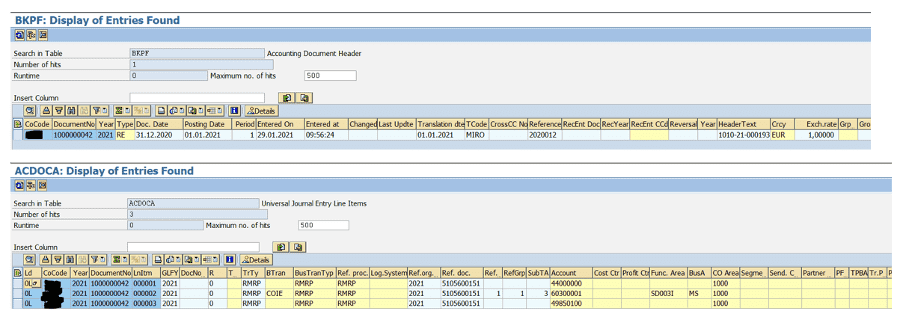
That’s it, that’s all! All FI and CO (I’ve outlined this a lot already, but a picture is better than 1000 words) combined in 2 tables. Isn’t it a beauty?
Furthermore, CO-PA is also embedded in the Universal Journal. CO-PA documents simply do not exist anymore.
SAP best practices recommend the use of an account-based CO–PA with real-time integration. It lets you acknowledge the impact on your result and margin in real time without having to settle the objects in CO-PA. The characteristics are derived and available the moment you post them in the system.
If you define a new characteristic, you can generate them in ACDOCA. You just must extend the CDS views to be able to view it in the standard reports.
With the Universal Journal and real-time CO-PA, you don’t have to wait for month-end to have your full P&L. You can also leverage the predictive analytics.
With the Universal Journal, the ‘old’ CO-PA tables are outdated.
See the table below for the comparison:
Tables | Costing based | Account based | SAP S/4HANA |
Actual line items | CE1XXXX | COEJ | ACDOCA |
Plan line items | CE2XXXX | COEP | ACDOCP |
Totals records per profitability segment | CE3XXXX | COSS, COSP | ACDOCA |
Profitability Segment definition | CE4XXXX | CE4XXXX | CE4XXXX |
Note that for the plan, SAP is working on a Plan Universal Journal (ACDOCP). It is still under construction and not all functionalities are available yet (referring to On-Premises 1909 version).
Conclusion
In a single entry (well let’s just say in one entry for a specific document) all the FI and CO information is centralized in that table.
It could have not been achieved without the power behind SAP HANA database technology.
SAP is continuing the work and is pushing toward the Plan Universal Journal. Thus, it will then be easier to plan (looking like it’s done in BPC) and compare the data with the actuals; especially when using the reports in BW embedded.
- S4IC is the commercial name of High-SEA company
- Open from Monday to Friday - 9am to 6pm
- Avenue Voltaire 3, 1300 Wavre
- +32 (0)2 880 91 10
- info@s4ic.com
- VAT : 0806 380 893
Copyright S4IC – 2021